Module 5: Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Why SMS Is Bad and Google Authenticator Is Good
Introduction: Why a Password Is Only Half the Protection
Imagine this scenario: you've created a super-complex 20-character password with every possible combination. Feeling secure? Don't be. In 2023, a hacker using SIM swapping gained access to a Coinbase user's account in just 15 minutes and withdrew $240,000. The password was perfect, but the protection wasn't.
The statistics are brutal: 81% of breaches occur due to weak or stolen passwords. But even a perfect password can be stolen through phishing, keyloggers, or database leaks. The only real protection is two-factor authentication (2FA).
However, not all 2FA methods are created equal. SMS codes, used by millions, actually provide an illusion of security while remaining extremely vulnerable. In this lesson, you'll learn why SMS 2FA is dangerous, how to properly set up Google Authenticator, and which methods provide maximum protection.
Key Fact: According to Google, two-factor authentication blocks 100% of automated attacks, 99% of bulk phishing attacks, and 66% of targeted attacks. This isn't optional — it's essential.

What Is Two-Factor Authentication and How Does It Work
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an account protection method that requires two independent ways to verify your identity instead of just one.
Three Authentication Factors
In cybersecurity, there are three types of factors:
- Something you know (Knowledge Factor) — password, PIN code, answer to a security question
- Something you have (Possession Factor) — phone, hardware key, smart card
- Something you are (Inherence Factor) — fingerprint, facial recognition, retina scan
2FA combines at least two of these factors. Typically this is:
- Password (something you know)
- + Code from an app/SMS (something you have)
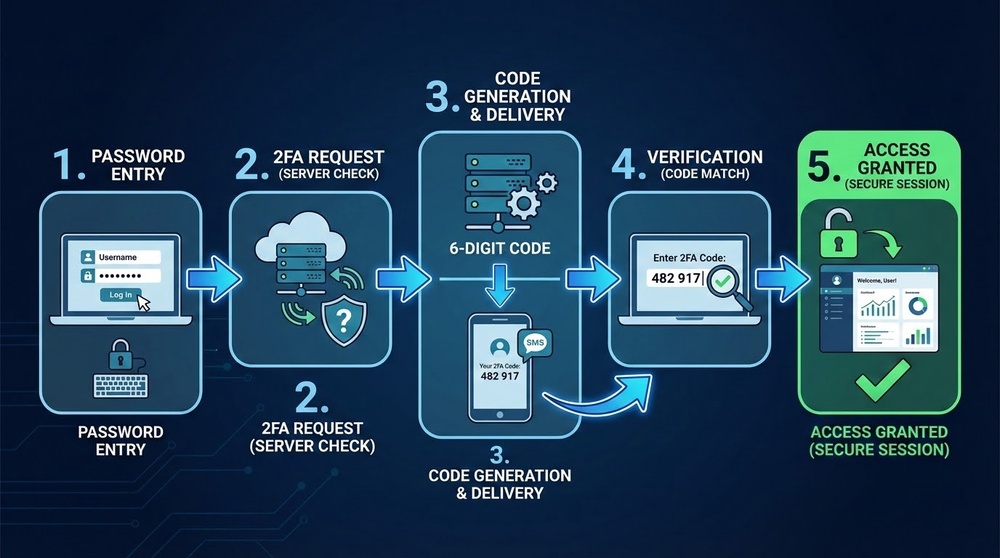
How the Login Process Works with 2FA
- Enter your login and password — first factor
- System requests second factor — verification code
- You generate/receive the code — via app, SMS, or hardware key
- Enter the code within a limited time — usually 30-60 seconds
- Access granted — only if both factors are correct
Why this is effective:
Even if a hacker steals your password through phishing or a database leak, they can't log in without access to the second factor — your phone or physical device.
Real-World Protection Example
In 2019, hackers stole a database containing 773 million email addresses and passwords (Collection #1). Users without 2FA were compromised instantly. Those with 2FA enabled remained protected — the stolen passwords were useless without the second factor.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication: From Worst to Best
Type 1: SMS Codes (⚠️ NOT Recommended)
The most common and most vulnerable method. A code is sent via text message to your phone number.
How it works:
- Enter your login and password
- System sends a 6-digit code to your number
- Receive the SMS and enter the code
- Gain access
Why SMS 2FA is dangerous:
1. SIM Swapping
A hacker calls your mobile carrier's office, impersonates you (social engineering), and requests a SIM card reissue to their number. The carrier transfers your number to the new SIM. Now all SMS codes go to the hacker.
Real Case — Michael Terpin vs AT&T:
In 2018, a crypto investor lost $24 million due to SIM swapping. Hackers compromised an AT&T employee's account and transferred Terpin's number to their SIM. They gained access to all accounts protected by SMS 2FA. Terpin filed a $200 million lawsuit against AT&T.
2. SS7 Vulnerability (SMS Interception)
The SS7 protocol, used by carriers for routing calls and SMS, has critical vulnerabilities. Hackers with access to the SS7 network can intercept SMS without physical access to the phone.
3. Real-Time SMS Phishing
Advanced phishing sites work in real-time: you enter login/password on a fake site → the scammer instantly enters them on the real site → you receive an SMS code → you enter it on the fake site → the scammer uses it on the real site → your account is compromised.
4. Malware on Your Phone
Trojans can intercept SMS messages and send them to attackers in real-time.
5. Social Engineering of Carrier Employees
Corrupt or deceived carrier employees perform SIM swaps for money at hackers' requests.
| Vulnerability | Attack Difficulty | Cost for Hacker | Frequency of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIM Swapping | Medium | $0-100 | Very High |
| SS7 Interception | High | $1,000-10,000 | Medium (targeted attacks) |
| Real-Time Phishing | Medium | $500 (infrastructure) | High |
| Malware | Low | $0-50 | High |
Conclusion: SMS 2FA is better than nothing, but it's the minimum level of protection. For cryptocurrency accounts, SMS 2FA is categorically insufficient. Use it only if there's no alternative.
Type 2: Email Codes (⚠️ Also Not Recommended)
A code is sent to your email instead of SMS.
Why this is bad:
- If email is compromised — access to everything
- Email is usually protected by the same password as the main service
- Slower than SMS (delivery can take minutes)
- Vulnerable to email account phishing
When acceptable: Only if email is protected by strong 2FA (TOTP or hardware key).
Type 3: TOTP Apps (✅ Recommended)
Time-based One-Time Password — codes are generated by an app on your device every 30 seconds.
Popular TOTP apps:
- Google Authenticator — most popular, simple
- Microsoft Authenticator — with cloud backup
- Authy — with cross-device sync
- 2FAS — open-source, feature-rich
- Aegis Authenticator — Android, open-source
- Raivo OTP — iOS, with iCloud backup
How TOTP works:
- During setup, the service generates a secret key
- You scan the QR code or enter the key into the app
- The app uses the TOTP algorithm + current time to generate a 6-digit code
- The code changes every 30 seconds
- The server knows your secret key and can verify the code's correctness
Advantages:
- Works offline — doesn't require internet or SMS
- No SIM-swapping risk — not tied to a phone number
- Cannot be intercepted — code is generated locally
- Resistant to phishing — if you notice the fake site in time
- Fast generation — code is always at hand
Disadvantages:
- Losing your phone = losing access (if no backup)
- Need to manually transfer to a new device
- Vulnerable to malware on the phone
- Some apps don't have cloud backup
Type 4: Push Notifications (✅ Good)
Instead of entering a code, you confirm login by tapping a button in the app.
Examples:
- Duo Mobile
- Microsoft Authenticator (push mode)
- Binance Verify
How it works:
- Enter your login and password
- A push notification arrives on your phone
- You see request details (device, location, IP)
- Tap "Approve" or "Deny"
Advantages:
- More convenient than entering codes
- Shows context (where the login is from)
- Harder to phish (victim sees details)
Disadvantages:
- Requires internet
- Vulnerable to advanced MitM attacks
- Push-fatigue attacks (attacker spams requests hoping for accidental approval)
Type 5: Hardware Security Keys (🏆 Best)
Physical USB/NFC devices providing maximum protection.
Popular brands:
- YubiKey — industry standard ($25-70)
- Google Titan Security Key — developed by Google ($30-50)
- Thetis FIDO U2F — budget option ($15-20)
- SoloKeys — open-source hardware ($20-50)
How it works:
- Enter your login and password
- System asks you to insert the key
- Connect YubiKey to USB
- Touch the sensor on the key
- Cryptographic signature confirms authenticity
Advantages:
- Impossible to phish — the key cryptographically verifies the site's domain
- No interception risk — doesn't transmit information over the network
- Protection from malware — physical confirmation
- Works without battery — powered by USB
- Durability — lasts for years
- Multiple protocols — FIDO U2F, FIDO2, WebAuthn
Disadvantages:
- Cost ($25-70 each)
- Need to carry it with you
- Loss = loss of access (need a backup key)
- Not all services support it
- Inconvenient on mobile devices (though NFC versions exist)
Professional Recommendation: For large amounts (>$50,000), use hardware keys. Buy 2 YubiKeys: carry the primary one with you, store the backup in a secure location. This is a $100-140 investment that will protect tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars.
| 2FA Method | Security | Convenience | Cost | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMS | ⭐⭐ Low | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ High | Free | ❌ Avoid |
| ⭐⭐ Low | ⭐⭐⭐ Medium | Free | ❌ Avoid | |
| TOTP Apps | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ High | Free | ✅ Minimum |
| Push Notifications | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very High | Free | ✅ Good |
| Hardware Keys | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Maximum | ⭐⭐⭐ Medium | $25-70 | 🏆 Best |
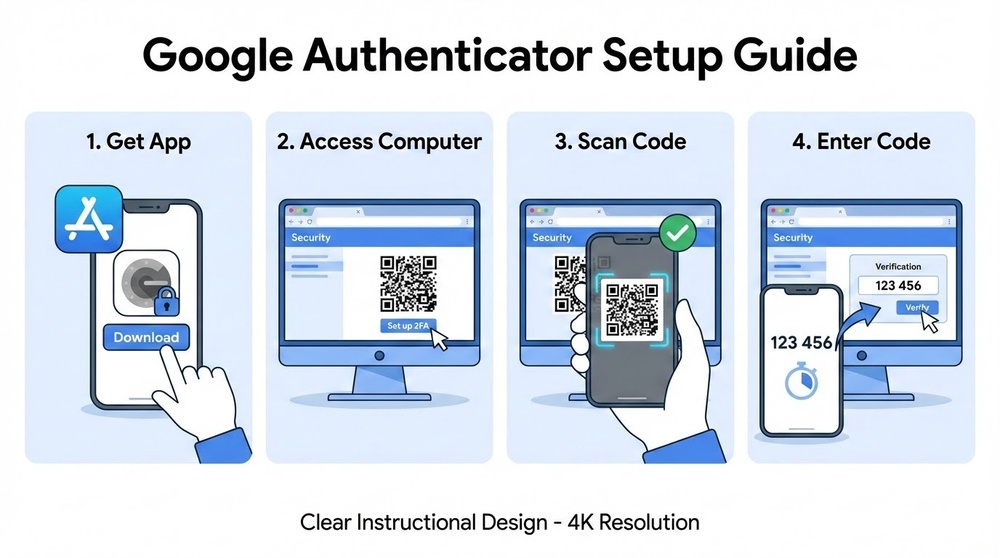
Step-by-Step Google Authenticator Setup
Let's set up 2FA properly using Google Authenticator — the most popular TOTP app.
Step 1: Install the App
- iOS: App Store → search "Google Authenticator" → install
- Android: Google Play → search "Google Authenticator" → install
Alternatives to consider:
- Authy — if you need cross-device sync
- 2FAS — if privacy matters (open-source, no tracking)
- Aegis (Android) — encrypted backup, fully offline
Step 2: Add Your First Account
Let's use Binance as an example:
- Log into Binance → go to Security Settings
- Find "Google Authenticator" → click "Enable"
- Binance will show a QR code and text key
- IMPORTANT: Write down the text key on paper (this is your backup!)
- Open Google Authenticator → tap "+" → "Scan QR code"
- Point your camera at the QR code on your computer screen
- Account added — you'll see a 6-digit code changing every 30 seconds
- Enter the current code in Binance to confirm
- 2FA activated ✅
Step 3: Save Backup Codes
Many services provide backup codes during 2FA setup — one-time codes for recovering access.
How to store backup codes:
- Write them on paper — store with your wallet seed phrase
- Print them and put in a safe
- Don't store in the cloud unencrypted
- If in a password manager — only with a master password + 2FA on the manager itself
Step 4: Set Up on All Critical Services
Where to enable 2FA first:
- ✅ All crypto exchanges (Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, Bybit)
- ✅ Email (Gmail, Outlook — the foundation of all security)
- ✅ Cloud storage (Google Drive, iCloud)
- ✅ Password managers (1Password, Bitwarden)
- ✅ Social media (Twitter, Telegram — to protect against compromise)
- ✅ Banking apps
Step 5: Test Your 2FA
Verify everything works:
- Log out of your account
- Try logging in again
- Enter password → system requests 2FA code
- Open Google Authenticator → enter the code
- If you logged in — setup successful ✅
If the code doesn't work:
- Check the time on your phone (must be synchronized)
- Make sure you enter the code before the 30 seconds expire
- In Google Authenticator: Settings → Time correction for codes → Sync now
2FA Backup: How Not to Lose Access
Losing your phone with Google Authenticator without a backup = losing access to all accounts. This is a catastrophe. Let's prevent it.
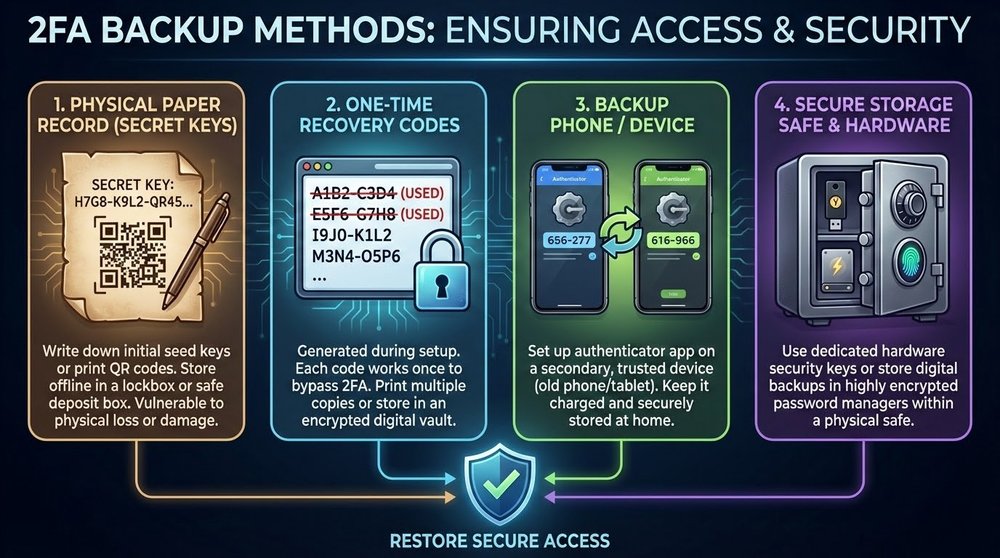
Method 1: Recording Secret Keys (Most Reliable)
What to do when setting up each account:
- When the service shows a QR code, it also shows a text key (a string of characters like "JBSWY3DPEHPK3PXP")
- Write this key on paper next to the service name
- Store the paper in a secure location (with your wallet seed phrase)
- If you lose your phone, manually enter the keys into a new app
Recording format:
Binance: JBSWY3DPEHPK3PXP Gmail: ABCDEF1234567890 Coinbase: XYZ789ABC123DEF
Method 2: Screenshot QR Codes (Less Secure)
You can screenshot QR codes and save them encrypted.
How to do it safely:
- Screenshot QR codes during setup
- Immediately transfer to encrypted storage (VeraCrypt container)
- Delete original screenshots from your gallery
- Never upload to the cloud unencrypted
⚠️ Danger: If screenshots leak, your 2FA is compromised.
Method 3: Using Authy (With Caution)
Authy allows syncing codes between devices via the cloud.
Advantages:
- Automatic backup
- Access from multiple devices
- Recovery if phone is lost
Disadvantages:
- Codes are stored in Authy's cloud (encrypted, but still)
- Vulnerable to Authy account hacking
- Requires phone number (SIM-swapping risk)
If using Authy:
- Set a strong master password
- Disable multi-device after initial setup
- Don't use for your most critical accounts
Method 4: Second Device with the Same Codes
When setting up 2FA on each service, scan the QR code on two devices simultaneously.
How to do it:
- Open the QR code on your computer screen
- Scan with your primary phone
- Scan with an old phone/tablet using the same QR code
- Now both devices generate identical codes
- Store the second device in a secure location as backup
Method 5: Service Backup Codes
Most services provide 10-20 one-time backup codes when setting up 2FA.
What to do:
- Save backup codes during initial setup
- Store in a password manager or on paper
- Use only in emergencies
- Generate new ones after use
Golden Backup Rule: At least two ways to recover access. Ideal: secret keys on paper + backup device + service backup codes. Redundancy in security is good.
Setting Up YubiKey Hardware Keys
For maximum protection of large holdings, consider hardware security keys.
Choosing the Right YubiKey Model
- YubiKey 5 NFC ($45-55) — universal model, USB-A + NFC for phones
- YubiKey 5C NFC ($55-70) — USB-C + NFC, for newer devices
- YubiKey 5C Nano ($65) — miniature USB-C, stays in laptop
- YubiKey Bio ($85-95) — with biometrics (fingerprint)
Recommendation: YubiKey 5 NFC — best price/functionality balance.
Setting Up YubiKey on Coinbase (Example)
- Buy 2 YubiKeys — primary and backup
- Log into Coinbase → Settings → Security
- Find "Security Keys" → Add Security Key
- Insert YubiKey into USB port
- Browser requests permission → Allow
- Touch the sensor on the YubiKey
- Give it a name (e.g., "YubiKey Primary")
- Repeat for the second key (backup)
- Test — log out and log in with YubiKey
Where to Store YubiKey
- Primary — on your keychain, always with you
- Backup — at home in a safe or bank safety deposit box
- Never store together — if you lose a bag with both keys, that's a problem
Services Supporting Hardware Keys
- ✅ Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini
- ✅ Google, Microsoft, Facebook
- ✅ GitHub, GitLab
- ✅ Dropbox, AWS
- ❌ Binance — not yet supported (use Google Auth)
- ❌ Most DeFi platforms — not supported
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake #1: Using SMS 2FA for Crypto Accounts
Why it's bad: SIM-swapping attacks are too common. For accounts with money, this is an unacceptable risk.
Solution: Switch to Google Authenticator at minimum, YubiKey at maximum.
Mistake #2: No Backup
Situation: Phone was stolen/lost/broken. Google Authenticator was only on it. No backup codes.
Result: Weeks of correspondence with support, providing documents, sometimes complete loss of access.
Solution: Write down secret keys during setup. Always.
Mistake #3: One Hardware Key Without a Backup
Situation: Bought one YubiKey, set it up on all services. Lost the key.
Result: Locked out of all accounts until getting a new key and lengthy recovery.
Solution: Always buy 2 keys, register both on each service.
Mistake #4: Storing Backup Codes in the Cloud
Why it's bad: If the cloud is hacked (Google Drive, Dropbox), they get access to 2FA backup codes.
Solution: Store backup codes offline or in an encrypted container with a separate password.
Mistake #5: Not Testing Recovery
Problem: Set up 2FA, wrote down codes, but never verified that recovery works.
Solution: Every six months, check:
- Do backup codes work?
- Can you restore 2FA from recorded keys?
- Does the backup YubiKey work?
Mistake #6: Giving 2FA Codes to "Helpers"
Situation: "Support" asks for a 2FA code for "security verification."
Reality: This is phishing. Real support NEVER asks for 2FA codes.
Rule: 2FA codes are only for logging into your own accounts. Never share them with anyone.
Mistake #7: Using 2FA Without a Strong Password
Misconception: "I have 2FA, my password can be simple."
Reality: 2FA is a second layer, not a replacement for the first. Weak password + 2FA < strong password + 2FA.
Solution: Generate random passwords of 16+ characters through a password manager.
Final 2FA Security Checklist
- Google Authenticator installed and set up on at least 3 critical services
- All crypto exchanges protected with TOTP 2FA (not SMS)
- Email protected with 2FA — this is the foundation of all security
- Secret keys recorded on paper for each account
- Service backup codes saved in a secure location
- Backup device set up or Authy with master password
- SMS 2FA disabled everywhere TOTP is available
- For holdings >$50K, YubiKey purchased (2 units)
- Recovery tested from backup codes/keys
- Strong passwords on all accounts (don't rely only on 2FA)
- I know that support NEVER asks for 2FA codes
- Time synchronized on devices with Google Authenticator
Conclusion: 2FA Is Not Optional — It's Essential
In a world where database breaches happen weekly and phishing sites become indistinguishable from originals, a password alone isn't enough. Two-factor authentication is the minimum security standard for anyone working with digital assets.
Remember the security hierarchy:
Password only < SMS 2FA < TOTP 2FA < Push 2FA < Hardware Keys
For cryptocurrency accounts, the minimum is TOTP (Google Authenticator). For serious amounts — hardware keys.
Invest an hour now to properly set up 2FA — it could save years of regret over lost funds.
In the next lesson, we'll cover what to do if you do get hacked: the action protocol for account compromise and whether stolen cryptocurrency can be recovered.







