Module 3: Phishing and Fake Websites: How to Avoid Handing Your Password to Hackers
Phishing in Cryptocurrency: Why It's the Number One Threat
Imagine this: you open Google, type "MetaMask," click on the first link, download the app, and enter your seed phrase to "recover" your wallet. Five minutes later, your account is empty. What happened? You landed on a perfect copy of the official website created by scammers.
According to Chainalysis research, over $1.7 billion in cryptocurrency was stolen through phishing in 2023. That's more than all exchange hacks combined. Why? Because hacking a well-protected system is difficult, but deceiving a person is easy.
The Core Principle of Phishing: Don't hack the technology—trick the people. The weakest link in any security system is the human. That's why even technically savvy users fall victim.
Phishing (from "fishing") is a cybercrime method where attackers impersonate legitimate companies or services to extract confidential data from victims: seed phrases, private keys, and passwords.

Anatomy of a Phishing Attack: How It Works
To protect yourself from phishing, you need to understand the psychology of scammers and the technical tricks they use.
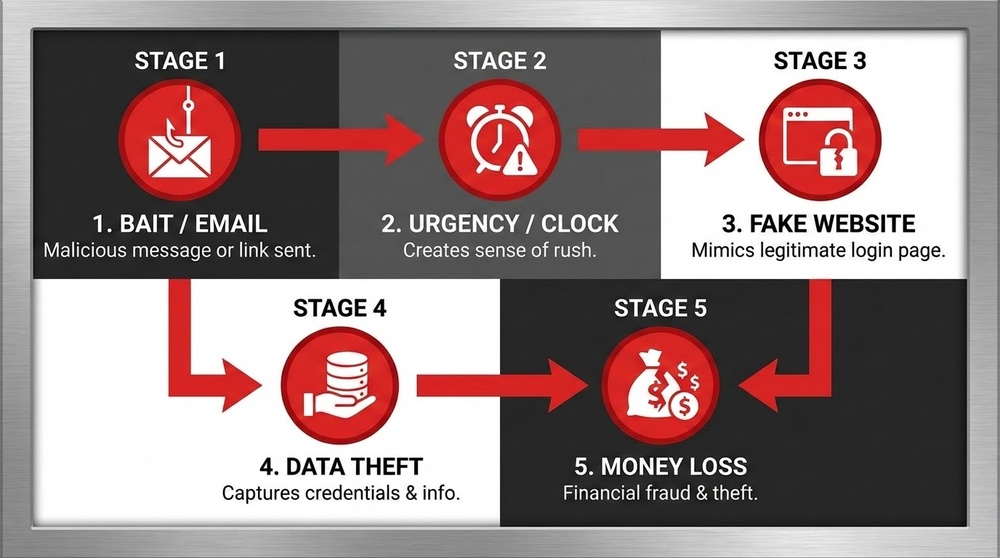
The Chain of a Successful Attack
Stage 1: Capturing Attention
Scammers use various channels to deliver phishing links to victims:
- Paid Google/Bing ads — fake sites buy top positions for key search terms
- Email campaigns — messages supposedly from exchanges, wallets, or blockchain projects
- SMS messages — "Your account has been blocked, click the link"
- Social media — fake Twitter/Telegram profiles posing as tech support
- Discord/Telegram bots — automated messages with "important information"
- Search engine results (SEO) — fake sites optimized for search engines
- YouTube videos — fake tutorial videos with links in the description
Stage 2: Creating Urgency
Scammers pressure emotions so victims act quickly without thinking:
- "Your account will be blocked in 24 hours"
- "Suspicious activity detected, verify your identity"
- "You won 0.5 BTC, claim it within an hour"
- "Urgent security update, act immediately"
- "Your funds are at risk, verification required"
Stage 3: Imitating Legitimacy
The fake website or email looks 99% like the original:
- Copied design, logos, colors
- Similar URL (metamask.com → metamаsk.com with a Cyrillic "а")
- SSL certificate (padlock in browser) — easy to get for free
- Official team photos
- Fake reviews and ratings
Stage 4: Data Collection
The victim enters confidential information:
- Seed phrase to "recover" the wallet
- Private key to "import" the address
- Exchange password + 2FA code
- Connects wallet to a malicious dApp
Stage 5: Stealing Funds
Data is instantly sent to scammers:
- Automated scripts drain all funds within seconds
- Money is transferred through mixers to hinder tracking
- By the time the victim realizes the scam — it's too late
The Psychology of Phishing
Scammers exploit basic human triggers:
- Greed — "free" airdrop, doubling funds
- Fear — threat of account lockout, losing money
- Urgency — "act now or lose your chance"
- Trust in authority — impersonating well-known brands
- Social proof — "10,000 users have already received"
- Curiosity — "secret information inside"
Types of Phishing Attacks in the Crypto Industry
Type 1: Fake Wallet and Exchange Websites
The most common type of attack. Scammers create an exact copy of a popular service.
Popular targets:
- MetaMask — the most popular Web3 wallet
- Trust Wallet, Exodus, Phantom
- Binance, Coinbase, Kraken
- Ledger Live, Trezor Suite
- Uniswap, PancakeSwap, other DEXs
What the attack looks like:
- URL: metamask.com → metamаsk.com (Cyrillic "а")
- URL: ledger.com → ledger-live.com, ledgerwallet.com
- URL: binance.com → binance-support.com, blnance.com
What they request:
- "Enter your seed phrase to recover your wallet"
- "Import your private key"
- "Connect your wallet to participate in the airdrop"
- "Complete KYC verification" (asking for documents + seed phrase)
Real case: In 2022, a user typed "phantom wallet" into Google, clicked on an ad (first position), and downloaded a fake extension. When "recovering" the wallet, they entered their seed phrase. They lost $140,000 in Solana and NFTs within 3 minutes.
Type 2: Email and SMS Phishing
Emails or messages supposedly from official services.
Typical scenarios:
- "Your Binance account has been temporarily blocked due to suspicious activity"
- "Urgent wallet update required for enhanced security"
- "You received a transfer of 0.5 BTC, confirm receipt"
- "Your Ledger device needs a critical firmware update"
- "Coinbase: unusual login to your account detected from Russia"
Signs of a phishing email:
- Sender: support@blnance.com (typo in domain)
- Generic greeting: "Dear user" instead of your name
- Grammatical errors and strange language
- Demand for urgent action
- Links look legitimate but lead to a different domain
- Request for confidential data
How to check a link in an email:
- Hover your cursor over the link (DO NOT click)
- At the bottom of the browser or in a tooltip, you'll see the real URL
- Check if it matches the link text
- If in doubt — go to the site directly, not via the link
Type 3: Fake Tech Support on Social Media
One of the most insidious types of phishing. You post on Twitter or Telegram about a problem, and instantly receive a reply from "official support."
How it works:
- You post: "@MetaMask help! I can't see my tokens"
- Within 30 seconds, an account @MetaMask_Support (fake) DMs you
- The profile looks official: logo, description, even a verification checkmark (fake)
- They ask you to click a link and "sync" your wallet
- Or they directly ask for your seed phrase "for diagnostic purposes"
Platforms where this is especially common:
- Twitter — fake accounts masquerading as @MetaMask, @Ledger, @binance
- Telegram — bots instantly respond to mentions of problems
- Discord — fake servers cloning official projects
- Reddit — fake moderators
Differences between fake and real support:
| Criteria | Real Support | Fake Support |
|---|---|---|
| Contact initiation | Waits for you to contact official channels | DMs you first |
| Data requests | NEVER asks for seed phrase/private key | Asks "for verification" |
| Resolution method | Provides instructions, links to documentation | Asks you to click a suspicious link |
| Urgency | Calm tone, no pressure | "Urgent!", "Within an hour", "Or you'll lose your funds" |
| Username | @MetaMask (official) | @MetaMask_Support, @MetaMask_Help (similar) |
Golden Rule of Tech Support: No legitimate crypto company will EVER DM you first. If someone messages you first — it's 100% a scam. Delete, block, don't respond.
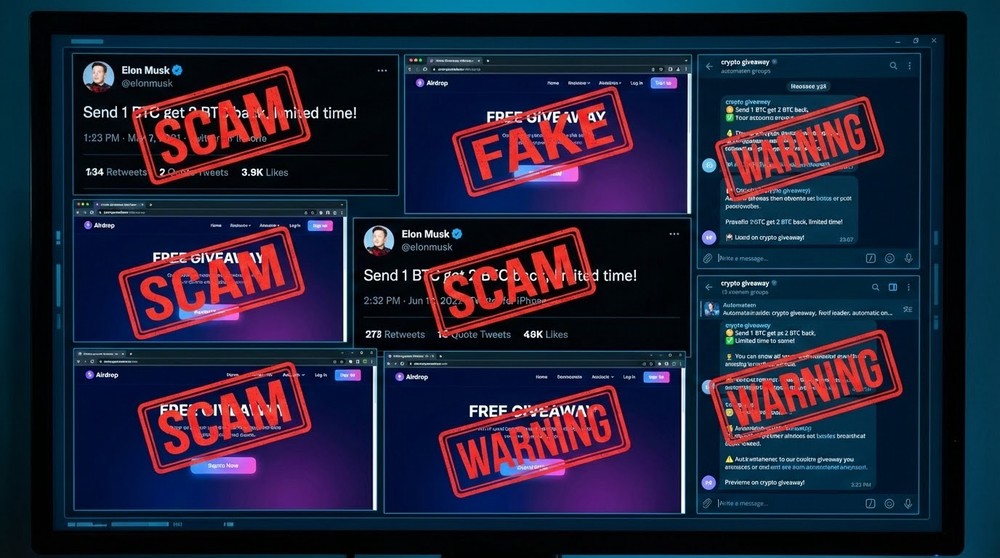
Type 4: Fake Airdrops and Giveaways
Exploiting greed is a powerful tool for scammers.
Popular schemes:
- "Doubling" cryptocurrency — "Send 0.1 BTC, get 0.2 BTC back"
- Fake airdrops — "Connect your wallet to receive 500 USDT"
- Fake NFT mints — "Free mint from Bored Ape, today only"
- Fake staking — "Stake tokens with 3000% APY"
Real case with Elon Musk:
Scammers hack verified Twitter accounts of celebrities or create high-quality fakes. They post: "To celebrate Tesla accepting Bitcoin, I'm giving away 10,000 BTC! Send 0.1-20 BTC to [address], get 2x back instantly!" People, seeing the "official" Elon Musk account, send money. Naturally, they get nothing back.
Signs of an airdrop scam:
- Requires you to send cryptocurrency first
- Asks you to connect your wallet to an unknown site
- Too generous conditions (giving away millions for free)
- Urgency — "only the next 100 people"
- Asks for seed phrase or private key
- Site has only existed for a few days
Type 5: Malicious dApps and Smart Contracts
Technically advanced phishing for DeFi users.
How it works:
- You connect your wallet to a fake DeFi protocol
- You sign a transaction without reading the terms
- In reality, you grant permission (approve) to withdraw ALL your tokens
- Scammers drain your funds whenever they want
Types of malicious permissions:
- Unlimited approve — permission to withdraw an infinite amount of tokens
- SetApprovalForAll — control over all NFTs in a collection
- Permit signatures — bypassing standard approve through a signature
- Proxy contracts — delegating control to an intermediary smart contract
Where it's found:
- Fake Uniswap, PancakeSwap, OpenSea sites
- Fake NFT mints of famous collections
- Fake staking platforms
- Malicious tokens in your wallet (appear on their own)
How to protect yourself:
- Use wallets with readable transactions (Rabby, Frame)
- Carefully read what you're signing
- Verify the contract address via Etherscan
- Regularly revoke old permissions via Revoke.cash
- Use a separate "hot" wallet for risky actions
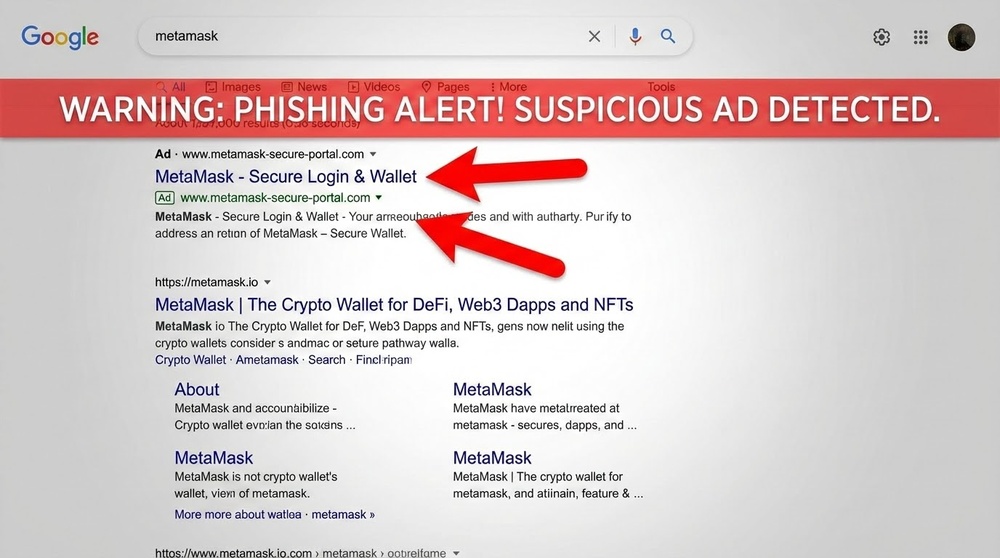
Type 6: Phishing via Google Ads and Search Advertising
One of the most insidious methods — hijacking search traffic.
Attack mechanics:
- Scammers buy Google ads for keywords like "metamask download," "binance login," "uniswap"
- Their fake site appears FIRST in results (with an "Ad" label)
- Users, without looking, click on the first link
- They land on a fake site that looks identical to the original
Why it works:
- People are used to clicking on the first results
- Google allows ads for phishing sites (moderation isn't perfect)
- Many don't notice the "Ad" label
- The URL can be very similar to the original
Protection:
- Add official sites to your browser bookmarks
- Never download software via ad links
- Check the URL three times before entering data
- Use ad blockers (uBlock Origin)
- Install extensions only from official stores
How to Spot a Phishing Website: A Verification Checklist
Learn to analyze websites in 30 seconds before entering any data.
Check #1: URL Address (The Most Important!)
What to look for:
- Correct domain
- ✅ metamask.io (correct)
- ❌ metamask.com, metamаsk.io (Cyrillic), metamask-wallet.com
- ✅ binance.com
- ❌ binance-support.com, blnance.com, binаnce.com (Cyrillic)
- Cyrillic characters — metamаsk.io looks like metamask, but the "а" is Cyrillic
- Extra words in the domain — an official site won't be ledger-wallet-support.com
- Unusual TLD — metamask.xyz, metamask.ru, metamask.app (could be a scam)
- Subdomains — metamask.phishing.com (the domain is phishing.com, not metamask)
Verification technique:
- Look at the URL in the address bar
- Read from right to left up to the first slash
- Make sure the root domain is correct
- Compare with the official address from documentation
Where to Find Official URLs
Don't trust search results! Sources of truth:
- CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap — verified links to projects
- Official Twitter with a blue checkmark (but be careful, checkmarks can be faked)
- GitHub repositories of the project
- Documentation (docs.) of the project
- Your old bookmarks (if created from verified sources)
Check #2: SSL Certificate (Not Enough, But Necessary)
What to check:
- Presence of a padlock in the address bar
- URL starts with https:// (not http://)
- Click on the padlock → view certificate information
- Check who the certificate was issued to
⚠️ Important to understand: An SSL certificate (https) does NOT guarantee safety! Scammers easily obtain free Let's Encrypt certificates. The padlock only means the connection is encrypted, not that the site is legitimate.
Check #3: Visual Signs
Red flags on a website:
- Grammatical errors — professional companies carefully proofread their texts
- Strange design — overlapping elements, low-quality images, broken layout
- Missing footer with company information, social media links
- Overly aggressive pop-ups — "connect your wallet NOW"
- No HTTPS on a site that handles finances
- Suspicious permissions — site asks for notification, camera access
Check #4: Domain Age and Reputation
Verification tools:
- whois.domaintools.com — when the domain was registered
- web.archive.org (Wayback Machine) — is there a site history
- scam-alert.io — database of known phishing sites
- Google Safe Browsing — built-in browser protection
Warning signs:
- Domain registered less than a month ago
- No history in the Wayback Machine
- Domain owner information is hidden (Privacy Protection)
- Site is registered to an individual, not a company
Check #5: Social Proof
What to research:
- Are there links to this site from the project's official Twitter?
- Is it mentioned on CoinGecko/CoinMarketCap?
- What are the reviews on Google, Trustpilot, Reddit?
- Is there activity on the project's social media?
- Is the project discussed by experienced crypto users?

Social Engineering: How Scammers Manipulate Your Mind
Phishing is not just technology, but also psychology. Understanding manipulation techniques helps you avoid being deceived.
Technique #1: Creating Urgency
How it works: When a person panics or rushes, they make irrational decisions.
Example phrases:
- "Your account will be blocked in 2 hours"
- "Only the first 100 participants will receive the reward"
- "Urgent security update by midnight"
- "Suspicious transaction detected, confirm within 30 minutes"
Countermeasure: With any urgency — pause. Real problems aren't solved in 30 minutes. Go to the official site directly (not via the link in the email) and verify the information.
Technique #2: Exploiting Authority
How it works: People tend to trust those who look like experts or representatives of authority/well-known companies.
Examples:
- An email supposedly from the Binance CEO
- A message from "MetaMask Security Team"
- A post from a fake Vitalik Buterin account
- An email with an official logo and signature
Countermeasure: Remember that company CEOs don't message regular users. Tech support doesn't message first. Verify real accounts on social media (blue checkmark, post history).
Technique #3: Playing on Greed
How it works: An offer "too good to be true" shuts down critical thinking.
Examples:
- "Send 1 ETH, get 2 ETH back"
- "Free airdrop of 1000 USDT"
- "Staking with 5000% annual yield"
- "You won 0.5 BTC in a lottery"
Countermeasure: If it sounds too good — it's a scam. Nobody gives away money for free. Legitimate projects don't promise unrealistic returns.
Technique #4: (Fake) Social Proof
How it works: "Everyone's already participating, join in!"
Examples:
- Fake counters "Already received: 43,721 people"
- Fake YouTube comments: "Wow, just received 1.5 BTC!"
- Bought followers and likes on social media
- Bot reviews on the website
Countermeasure: Verify the authenticity of reviews. Look for discussions on independent platforms (Reddit, specialized forums). Analyze whether comments look templated.
Technique #5: Emotional Pressure
How it works: Fear, panic, FOMO (fear of missing out) shut down logic.
Examples:
- "Your funds are in danger!"
- "Last chance to participate"
- "While you're thinking, others are already earning"
- "Don't miss the opportunity of a lifetime"
Countermeasure: Emotional messages are a red flag. Legitimate companies communicate neutrally and professionally. Take a deep breath and engage your critical thinking.
Phishing Protection: Practical Tools and Habits
Basic Security Measures
1. Use Browser Bookmarks
- Add all frequently used sites to bookmarks
- ALWAYS access them via bookmarks, not through search
- Create a "Crypto" folder with verified links
- Sync bookmarks across devices
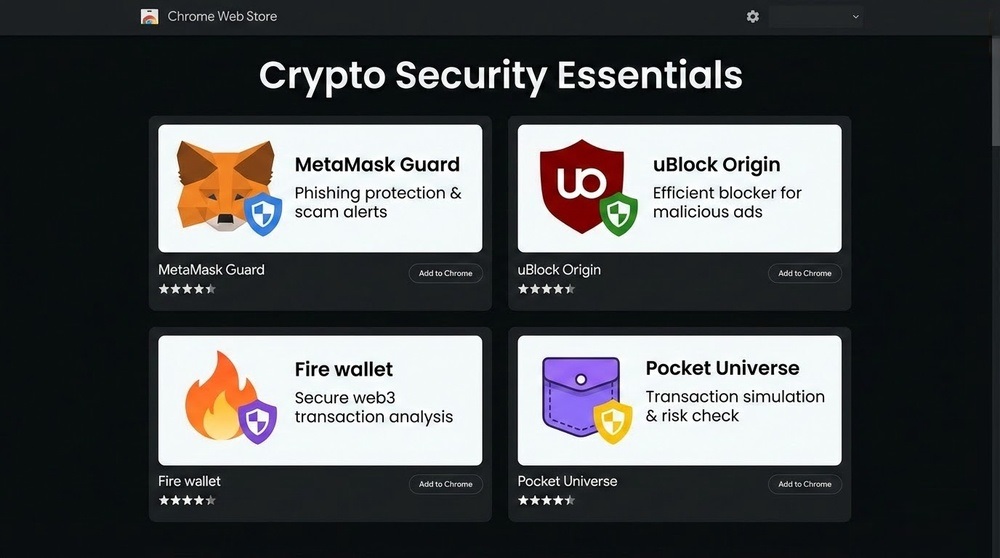
2. Install Security Extensions
- MetaMask Guard — warns about phishing sites
- Fire (wallet.fire.com) — scans transactions before signing
- Pocket Universe — simulates transactions, shows consequences
- uBlock Origin — blocks ads (including phishing ads)
- CryptoScamDB — checks sites against a database of known scams
3. Use Separate Browsers/Profiles
- Main browser — for regular work
- Separate profile/browser — only for cryptocurrency
- Don't install unnecessary extensions in the crypto browser
- Incognito mode for one-time checks of unfamiliar sites
4. Two-Factor Authentication (BUT NOT SMS)
- Use Google Authenticator or Authy
- Never rely on SMS codes (easily intercepted)
- For exchanges — hardware keys (YubiKey)
- Save backup codes in a secure place
5. Verify Contract Addresses
- Before interacting with a dApp, verify the contract address on Etherscan
- Compare with the project's official documentation
- Pay attention to the contract's age and number of transactions
- Read comments and warnings in the explorer
Advanced Protection Techniques
1. Separate Wallets for Different Purposes
- Cold wallet — main capital, never connects to dApps
- Warm wallet — for DeFi with verified protocols
- Hot/burner wallet — for risky actions (new NFT mints, airdrops)
- Transfer funds between wallets as needed
2. Regular Permission Audits
- Once a month, check Revoke.cash or Etherscan Token Approvals
- Revoke permissions from unused protocols
- Pay attention to Unlimited Approvals — replace with limited ones
- After using a new dApp, immediately revoke the permission
3. Transaction Analysis Before Signing
- Use wallets with readable transaction displays (Rabby, Frame)
- Don't sign transactions blindly
- If you don't understand what a transaction does — don't sign it
- Check the recipient address three times
4. Wallet Monitoring
- Set up notifications via Etherscan Alerts
- Use Zerion or Zapper to track activity
- Act immediately on suspicious transactions
- Check transaction history once a week
What to Do If You've Fallen Victim to Phishing
Panic is the worst advisor. Follow a clear protocol.
The First 5 Minutes (Critically Important)
- Don't close the phishing site tab — you'll need it for the investigation
- Open a new tab — go to the official wallet website
- Create a new wallet with a new seed phrase immediately
- Transfer funds — start with the most valuable assets
- Don't waste time thinking — every second counts
The First Hour
- Transfer ALL assets to new addresses (tokens, NFTs, staking)
- Revoke all approve permissions from old addresses via Revoke.cash
- Change passwords on exchanges if you used the same email/passwords
- Scan your computer with antivirus (Malwarebytes, Kaspersky)
- Take a screenshot of the phishing site for the report
The First Day
- Report the phishing:
- Google Safe Browsing: safebrowsing.google.com/safebrowsing/report_phish
- CryptoScamDB: cryptoscamdb.org/report
- Twitter of the project that was impersonated
- Regulator (if a significant amount)
- Warn the community — a post on Twitter/Reddit can save others
- Analyze what went wrong — how to avoid it in the future
- Check other devices — maybe not just the computer is infected
Can Stolen Funds Be Recovered?
Reality: In 99% of cases — no. Cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible.
Exceptions (minimal chances):
- If funds are still at the scammer's address — some exchanges may freeze them upon receiving a complaint
- If funds are on a centralized exchange — contact support with evidence of fraud
- If the amount is very large — hire a blockchain forensics company (Chainalysis, CipherTrace)
- Smart contract with a vulnerability — theoretically, it can be exploited for recovery
Practical steps:
- Track the scammer's address via Etherscan
- If funds went to a known exchange — write to their support
- File a report with cyber police (for statistics, don't expect real results)
- Publish the scammer's address on CryptoScamDB
The Bitter Truth: Time spent trying to recover funds is often wasted. It's better to direct your energy toward learning from mistakes and strengthening your defenses for the future. In cryptocurrency, prevention is 1000 times more effective than cure.
Final Checklist: How to Avoid Becoming a Phishing Victim
- All crypto sites are bookmarked — I only access them through bookmarks
- Security extensions installed — MetaMask Guard, uBlock Origin
- I know that tech support never DMs first
- I never give my seed phrase to anyone — not a friend, not "support"
- I check the URL three times before entering data
- I don't click on ads when searching for crypto sites
- I don't participate in "giveaways" and "doublings"
- I read transactions before signing in dApps
- I regularly revoke old approvals via Revoke.cash
- I use separate wallets for different purposes
- I enabled 2FA everywhere (Google Authenticator, not SMS)
- When there's urgency, I pause and verify the information
- I don't trust "too good to be true" offers
- I verify contract addresses on Etherscan
- My computer is protected by antivirus
Conclusion: In Cryptocurrency, Vigilance Is a Skill
Phishing evolves every day. Scammers are becoming more inventive, their fakes are higher quality, and their psychological techniques are more sophisticated. There's no universal solution that protects 100%.
But there is a universal principle: healthy paranoia. In cryptocurrency, it's better to double-check ten times and look like a paranoid than to not check once and lose everything.
Remember: legitimate companies don't need your seed phrase. Real airdrops don't require you to send money first. Official tech support doesn't DM first. If something looks too good to be true — it's a scam.
In the next lesson, we'll cover scam tokens and financial pyramids — how to recognize a fraudulent project before you invest your money.







