Module 3: Ethereum (ETH) and Smart Contracts: Why It's a Revolution
Introduction: Ethereum — More Than Just a Cryptocurrency
If Bitcoin is digital gold and a store of value, then Ethereum (ETH) is an entire decentralized computer where you can build applications, issue tokens, and automate financial operations without intermediaries.
Imagine this: you can enter into an agreement with a stranger on the other side of the planet, and that agreement executes automatically—no lawyers, banks, or courts needed. Sounds like science fiction? Welcome to the world of smart contracts.
💡 Key Insight: Ethereum expanded blockchain capabilities far beyond simple money transfers. It created a platform where anyone can program money and build decentralized applications.

The History of Ethereum: From Idea to Revolution
Ethereum's story began with a young programmer named Vitalik Buterin—a Canadian of Russian origin. In 2013, when he was just 19 years old, he published a whitepaper describing the concept of a next-generation blockchain.
Key Milestones in Ethereum's History
- 2013 — Vitalik Buterin publishes the Ethereum concept
- 2014 — Crowdfunding campaign (ICO) raises over $18 million
- 2015 — Ethereum mainnet launches (Frontier version)
- 2016 — The DAO hack and subsequent hard fork splits the network into Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC)
- Later — Transition to Proof of Stake consensus mechanism (The Merge)
🎯 Fun Fact: Vitalik originally wanted to add smart contract functionality to Bitcoin, but the community rejected his idea. So he decided to build his own blockchain from scratch.

How Is Ethereum Different from Bitcoin?
Many beginners confuse Bitcoin and Ethereum, thinking they're just "different coins." In reality, they're fundamentally different technologies with different purposes.
| Feature | Bitcoin (BTC) | Ethereum (ETH) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Purpose | Digital money, store of value | Platform for decentralized applications |
| Creator | Satoshi Nakamoto (anonymous) | Vitalik Buterin (public) |
| Programming Language | Limited scripting language | Solidity (full-featured smart contract language) |
| Maximum Supply | 21 million BTC | No hard cap (but has a burning mechanism) |
| Block Time | ~10 minutes | ~12-14 seconds |
| Smart Contracts | Very limited | Fully functional (Turing-complete) |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
Simple Analogy
Bitcoin is like gold in a digital vault. You store it, transfer it, but it's simply value.
Ethereum is like an operating system (Windows or Android) for the financial world. You can run programs, games, applications—anything you want.
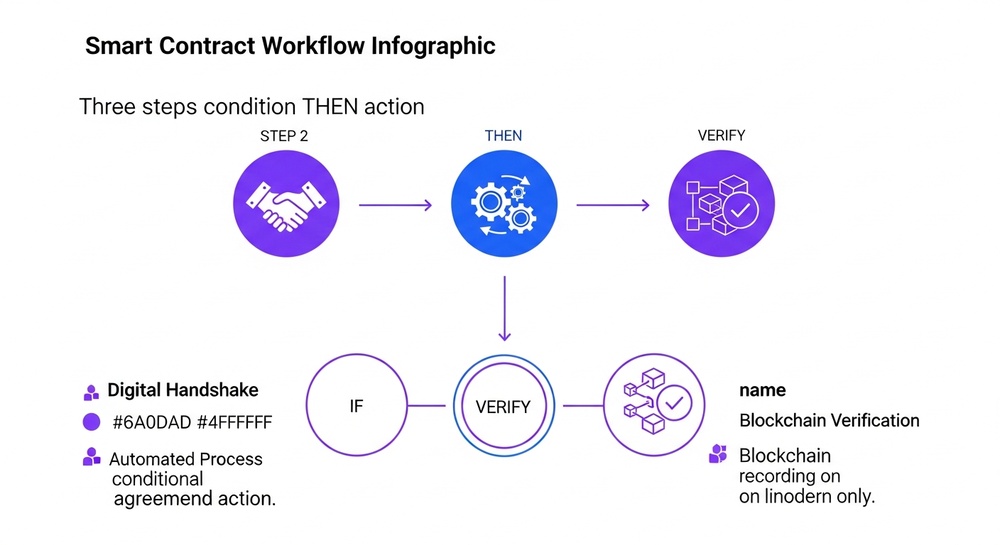
What Is a Smart Contract? Explained Simply
A smart contract is a computer program that automatically executes when certain conditions are met. It's recorded on the blockchain and operates without intermediaries.
How Does It Work in Practice?
Imagine a traditional apartment rental agreement:
- You pay a deposit to the landlord
- The landlord gives you the keys
- At the end of the rental, you return the keys
- The landlord (maybe) returns your deposit
The problem? Trust. What if the landlord doesn't return the deposit? You'd have to go to court, spending time and money.
Now imagine a smart contract:
- You send the deposit to the smart contract (not the landlord!)
- The smart contract automatically unlocks the apartment's digital lock
- When the rental period ends, the contract verifies conditions
- If everything checks out—the deposit automatically returns to you
🔐 Key Principle: A smart contract is code that executes automatically and immutably. Nobody (not even the creator) can change the conditions after deployment. This is called "Code is Law."
The Smart Contract Formula
Smart Contract Logic
IF [condition A is met] → THEN [action B automatically happens]
- IF 100 ETH is received → THEN ship the product to the buyer
- IF date X arrives → THEN transfer salary to the employee
- IF player scores 1000 points → THEN issue an NFT reward
Real-World Smart Contract Use Cases
Smart contracts aren't abstract technology. They're already transforming entire industries. Here are the main applications:
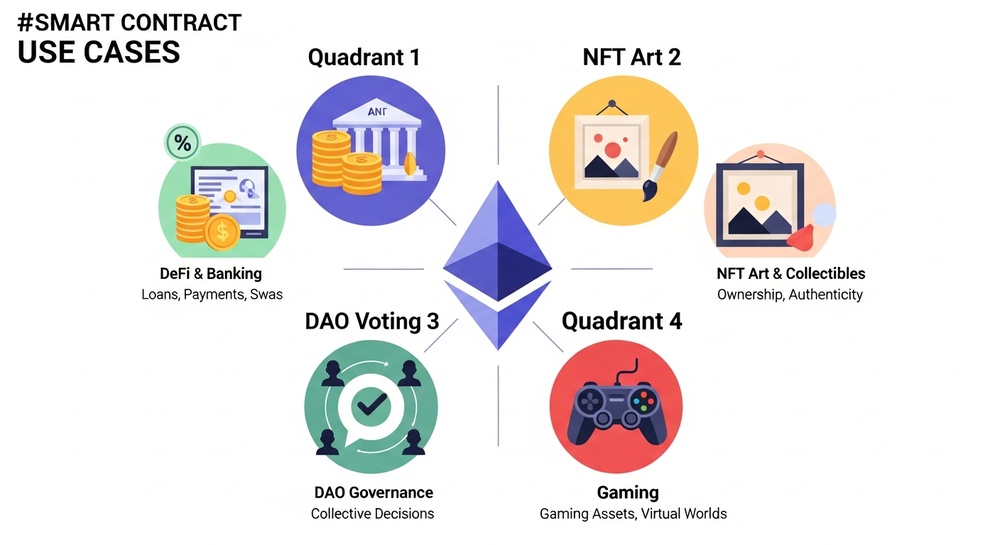
1. DeFi — Decentralized Finance
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) refers to financial services without banks. Loans, borrowing, currency exchange, deposits—everything runs on smart contracts.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) — swap tokens without intermediaries (Uniswap, SushiSwap)
- Lending Platforms — lend assets and earn interest (Aave, Compound)
- Stablecoins — tokens pegged to the dollar (DAI is created through smart contracts)
- Yield Farming — strategies to maximize returns on crypto assets
💰 Why This Matters: In a traditional bank, getting a loan requires documents, verification, and time. In DeFi, you can get a loan in 30 seconds with just cryptocurrency as collateral.
2. NFTs — Non-Fungible Tokens
NFT (Non-Fungible Token) is a unique digital asset whose authenticity is guaranteed by the blockchain. Smart contracts store ownership information and transfer history.
- Digital Art — paintings, music, videos
- Gaming Items — weapons, characters, virtual land in metaverses
- Collectibles — sports cards, rare items
- Documents — diplomas, certificates, event tickets
3. DAOs — Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is an organization governed by smart contracts and token holder voting. No directors, no offices—just code and community.
- Members vote on proposals using tokens
- Treasury is managed by smart contracts
- Decisions execute automatically
4. Other Applications
- Insurance — automatic payouts when insured events occur
- Supply Chain — tracking goods and automatic payments
- Voting — transparent and tamper-proof elections
- Royalties — creators automatically receive a percentage from every resale
Gas in Ethereum: Paying for Computation
Every operation on the Ethereum network requires computational resources. Gas is the unit measuring the work performed by network nodes.
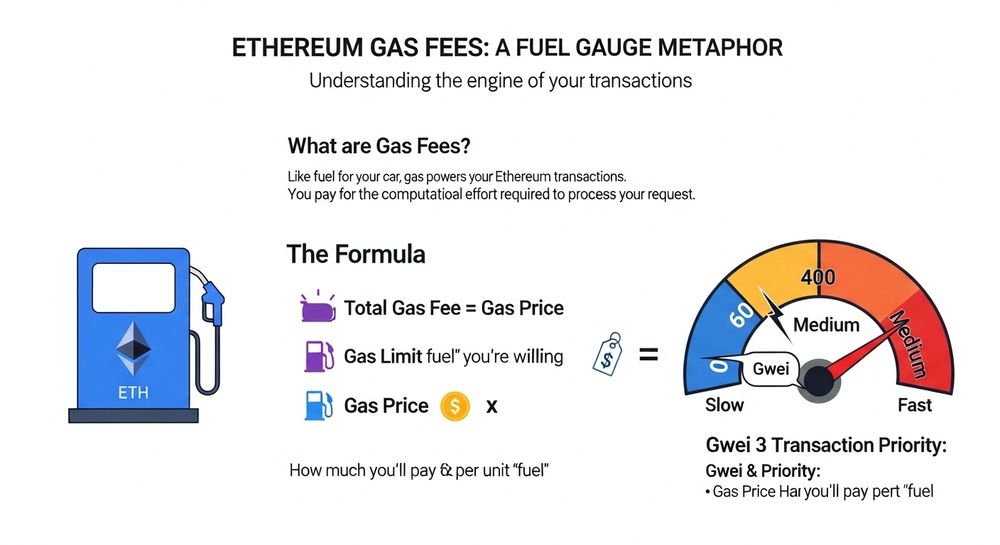
How Does Gas Work?
- Gas Limit — the maximum amount of gas you're willing to spend
- Gas Price — the price per unit of gas (measured in Gwei)
- Fee = Gas Used × Gas Price
Car Analogy
Imagine you're driving a car:
- Gas Limit — the size of your fuel tank
- Gas Price — the price per gallon of fuel
- Gas Used — how much fuel you actually used for the trip
The more complex the smart contract, the more "fuel" it consumes.
Why Are Fees Sometimes High?
When many people want to use the network simultaneously, they compete for block space. Whoever offers a higher gas price gets processed faster. This creates "fee wars" during periods of high demand.
⚡ The Solution: Layer 2 scaling solutions have been developed to reduce fees—Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon. They process transactions off the main chain and only record the final result.
ERC-20: The Token Standard on Ethereum
ERC-20 is a technical standard for creating tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Thanks to it, thousands of projects can issue their own cryptocurrencies without building a separate blockchain.
What Does the ERC-20 Standard Provide?
- Compatibility — all ERC-20 tokens work with any Ethereum wallet or exchange
- Simplicity — you can create a token in minutes
- Functionality — standard set of functions: transfer, balanceOf, approve
Popular ERC-20 Tokens
| Token | Purpose | Category |
|---|---|---|
| USDT (Tether) | Stablecoin pegged to the US dollar | Stablecoin |
| USDC | Stablecoin by Circle and Coinbase | Stablecoin |
| LINK (Chainlink) | Oracles for smart contracts | Infrastructure |
| UNI (Uniswap) | Governance token for Uniswap DEX | DeFi |
| SHIB (Shiba Inu) | Meme coin | Meme |
Other Token Standards
- ERC-721 — standard for NFTs (unique tokens)
- ERC-1155 — hybrid standard for NFTs and fungible tokens
- ERC-4626 — standard for tokenized vaults
Ethereum 2.0 and the Transition to Proof of Stake
One of the most significant events in Ethereum's history was the transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This upgrade is called "The Merge."

What Changed After The Merge?
❌ Before (Proof of Work)
Miners solved complex puzzles, consuming massive amounts of electricity. The network used as much energy as a small country.
✅ After (Proof of Stake)
Validators "stake" their ETH as collateral for honest behavior. Energy consumption dropped by ~99.95%.
Benefits of Proof of Stake
- Eco-Friendly — energy consumption reduced by 99.95%
- Accessibility — no need to buy expensive mining equipment
- Security — attacking the network became economically unfeasible
- Staking — ETH holders can earn passive income
📊 To Participate in Ethereum Staking: To become a full validator, you need to stake 32 ETH. However, staking pools exist where you can participate with any amount.
Risks and Limitations of Ethereum
Despite all its advantages, Ethereum has challenges you should know about:
Main Challenges
- Scalability — the mainnet processes ~15-30 transactions per second (Visa handles thousands)
- High Fees — during peak times, gas can cost tens of dollars
- Smart Contract Bugs — code can't be changed after deployment; bugs can lead to lost funds
- Competition — Solana, Cardano, Avalanche, and other blockchains offer alternatives
How to Protect Yourself?
- Only use verified and audited smart contracts
- Never invest more than you can afford to lose
- Research projects before interacting with them
- Store large amounts on hardware wallets
Why Ethereum Is a Revolution
Let's summarize. Ethereum changed the world of cryptocurrency and technology for several reasons:
1. Programmable Money
For the first time in history, money became programmable. You can create a token with any rules: automatic taxes, profit distribution, voting.
2. Decentralized Trust
No more need to trust banks, lawyers, or intermediaries. Code is law, and it executes the same way for everyone.
3. Open Finance
Anyone in the world with internet access can use financial tools: loans, investments, insurance—without a bank account or documents.
4. A New Economy
NFTs, metaverses, GameFi, DAOs—all of this became possible thanks to smart contracts on Ethereum.
🚀 Conclusion: Ethereum isn't just "another cryptocurrency." It's the foundation of a new decentralized economy. Understanding how it works is essential knowledge for anyone who wants to master crypto.
Key Terms from This Lesson
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Ethereum (ETH) | Blockchain platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications |
| Smart Contract | A program that automatically executes when conditions are met |
| Gas | Unit measuring computational work on the Ethereum network |
| ERC-20 | Standard for creating fungible tokens on Ethereum |
| DeFi | Decentralized financial services on blockchain |
| DAO | Organization governed by smart contracts and community voting |
| The Merge | Ethereum's transition from PoW to PoS |
| Layer 2 | Scaling solutions built on top of the main blockchain |
What's Next?
Now you understand why Ethereum is called the "world computer" and how smart contracts are changing the game. In the next lesson, we'll explore altcoins, stablecoins, and meme coins—learning what makes them different and why they exist.
Test Yourself
- How is Ethereum fundamentally different from Bitcoin?
- What is a smart contract in simple terms?
- Why is gas needed on the Ethereum network?
- What is ERC-20 and why does it matter?
- What benefits did the transition to Proof of Stake bring?