Module 6: Bitcoin Halving: Why Everyone's Talking About It
Introduction: The Mysterious Word "Halving"
If you've spent any time exploring cryptocurrencies, you've probably heard the word "halving". Every few years, the crypto community literally holds its breath in anticipation of this event. News feeds are flooded with headlines, analysts make predictions, and investors reconsider their strategies.
But what exactly is a halving? Why does it happen? And most importantly — why does it matter so much for anyone who owns Bitcoin or is planning to buy some?
In this lesson, we'll break down the halving mechanism in simple terms, look at the history of past events, understand their impact on the market, and learn how to use this knowledge in your investment decisions. By the end of this lesson, you'll understand halving better than 90% of crypto enthusiasts!

💡 Key Takeaway: Halving isn't just a technical event. It's a programmed scarcity mechanism that makes Bitcoin a unique asset in human history and determines its long-term value.
What is Bitcoin Halving: Explained Simply
Imagine you work at a gold mine. For each day of work, you're paid a certain amount of gold. Now imagine that every 4 years, your salary automatically gets cut in half. First, you receive 100 grams of gold per day, then 50, then 25, then 12.5, and so on.
That's exactly how halving works in the Bitcoin world, except instead of gold miners — there are miners, and instead of a salary — there's a block reward.
Technical Definition
Halving is an event programmed into Bitcoin's code where the reward miners receive for creating a new block is cut exactly in half. This event occurs automatically every 210,000 blocks, which roughly corresponds to 4 years.
The Math Behind Halving
Why approximately 4 years? Let's calculate:
- A new block is created approximately every 10 minutes
- There are 1,440 minutes in a day, meaning ~144 blocks are created daily
- 210,000 blocks ÷ 144 blocks per day = 1,458 days
- 1,458 days ÷ 365 = approximately 4 years
This isn't a coincidence — Satoshi Nakamoto deliberately built this interval into the protocol!
How It Works in Practice
When a miner successfully mines a new block (solves a complex cryptographic puzzle), they receive a reward in the form of newly created bitcoins. This is the only way new BTC enters circulation.
Before a halving, a miner might receive, for example, 6.25 BTC per block. After the halving, this reward becomes 3.125 BTC. The amount of new bitcoins entering circulation is cut in half.
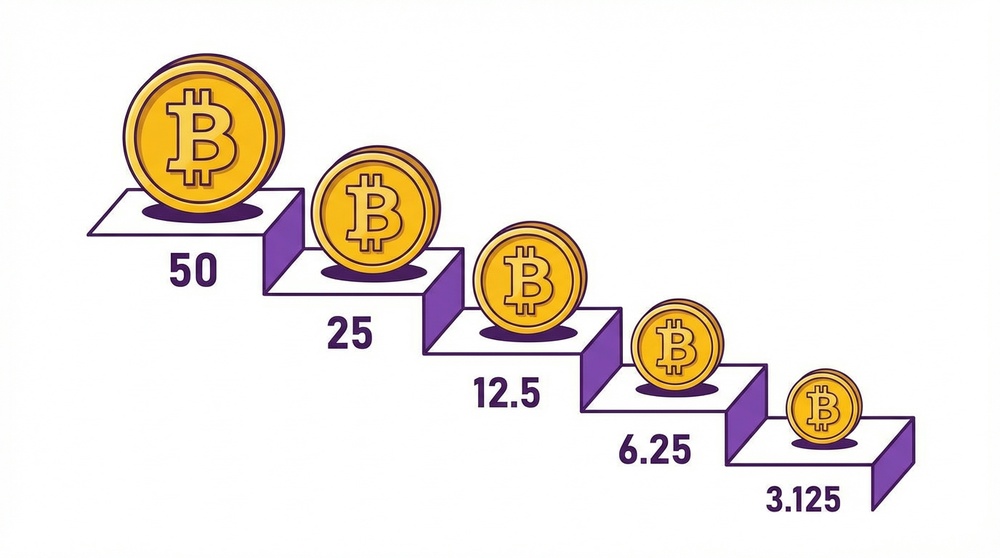
History of Halvings: From 50 BTC to Crumbs
Since Bitcoin's launch in 2009, several halvings have occurred. Each one is a milestone in cryptocurrency history. Let's examine them in detail:
| Event | Date (Approximate) | Block # | Reward Before | Reward After |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genesis | January 2009 | 0 | — | 50 BTC |
| 1st Halving | November 2012 | 210,000 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC |
| 2nd Halving | July 2016 | 420,000 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC |
| 3rd Halving | May 2020 | 630,000 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC |
| 4th Halving | April 2024 | 840,000 | 6.25 BTC | 3.125 BTC |
| 5th Halving | ~2028 | 1,050,000 | 3.125 BTC | 1.5625 BTC |
Interesting Facts About Early Halvings
The First Halving (2012) went almost unnoticed by the general public. Bitcoin was worth around $12 at the time, and the crypto community was tiny. However, within a year after this event, the price increased more than 100 times!
The Second Halving (2016) attracted more attention. Traders and analysts began noticing a pattern: after the reward reduction, the price tends to rise. This event preceded the famous 2017 bull run.
The Third Halving (2020) became a true media event. It was broadcast live, and companies worldwide hosted online parties. After it, Bitcoin reached all-time highs.

Why Satoshi Created Halving: The Philosophy of Scarcity
To understand why halving is so important, we need to go back to the very beginning — to the ideas of Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin's creator.
The Problem with Traditional Money
Traditional (fiat) currencies, such as dollars, euros, or pounds, have one critical vulnerability: central banks can print unlimited amounts of them. This leads to inflation — the gradual devaluation of money.
Think about it: $100 in 1970 could buy far more goods than the same $100 today. Your savings are slowly but surely losing purchasing power.
💵 Fiat Money (Inflationary Model)
Supply is unlimited. The central bank can print as much new money as it wants. Over time, this leads to inflation and devaluation of savings.
₿ Bitcoin (Deflationary Model)
Supply is strictly limited to 21 million coins. Halving gradually slows emission, making BTC an increasingly scarce asset.
Gold Standard 2.0
Satoshi Nakamoto based the model on gold — an asset that has preserved value for millennia precisely because of its scarcity. Gold cannot be "printed"; it must be mined, and this becomes more difficult each year.
Bitcoin went even further:
- Its supply isn't just limited — it's known in advance and unchangeable
- The emission rate is programmatically slowed every 4 years
- No government or organization can change these rules
- The last bitcoin will be mined around 2140
🎯 Satoshi Nakamoto Quote: "The total circulation will be 21,000,000 coins. It'll be distributed to network nodes when they make blocks, with the amount cut in half every 4 years."
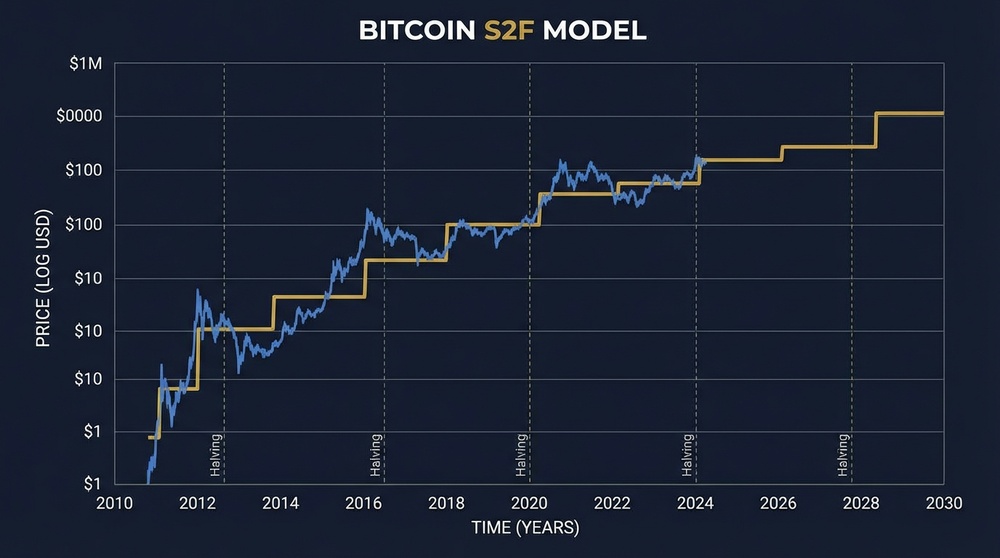
The Stock-to-Flow Model
Economists use the concept of Stock-to-Flow (S2F) — the ratio between an asset's existing supply and its annual production. The higher this ratio, the scarcer the asset is considered.
| Asset | Stock-to-Flow | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Silver | ~22 | Takes 22 years to double the supply |
| Gold | ~62 | Takes 62 years to double the supply |
| Bitcoin (after 4th halving) | ~120 | The rarest asset in history! |
With each halving, Bitcoin's Stock-to-Flow ratio increases, making it scarcer than gold. This is a fundamental economic property that cannot be changed.
Halving's Impact on Price: What History Tells Us
Now let's talk about what interests most people: how does halving affect Bitcoin's price?
Basic Economics: Supply and Demand
Halving directly affects the supply of new bitcoins:
- Before halving: X new BTC enter the market daily
- After halving: X/2 new BTC enter the market daily
- If demand stays the same or increases while supply decreases — price tends to rise
This is a basic economic law that works for any commodity: scarcity creates value.
The Numbers Speak for Themselves
Look at the price dynamics after each halving:
- After 1st Halving (2012): price rose from ~$12 to ~$1,100 (~90x increase)
- After 2nd Halving (2016): price rose from ~$650 to ~$20,000 (~30x increase)
- After 3rd Halving (2020): price rose from ~$9,000 to ~$69,000 (~7.5x increase)
Important: Past performance does not guarantee future results!
Why Growth Isn't Instant
Many newcomers expect the price to skyrocket immediately after halving. But history shows a different picture:
- Before halving: the market often "prices in" expectations ahead of time
- At the moment of halving: there may be volatility, but usually no sharp spike
- 6-18 months after: historically, this is the period of greatest growth
- Correction: after reaching peaks, significant declines usually follow
This is explained by the fact that supply reduction is a gradual process. Price pressure builds over time as fewer new coins enter the market.
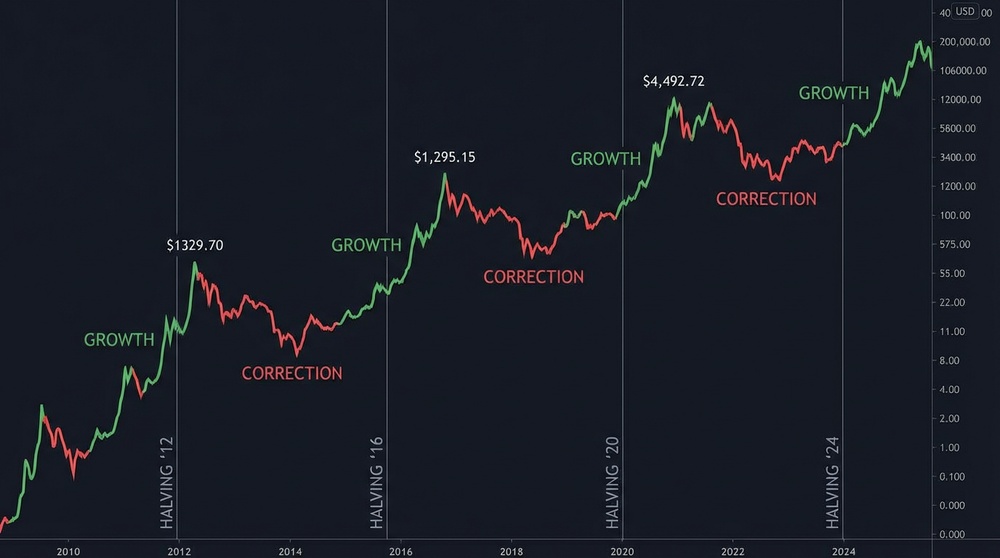
The "Four-Year Cycle" Theory
Based on observations, a popular theory about Bitcoin's four-year market cycles has emerged:
- Year 1 (halving year): Accumulation, moderate growth
- Year 2: Bull market, significant growth, euphoria
- Year 3: Peak reached, correction begins
- Year 4: Bear market, accumulation before the next halving
⚠️ Important Warning: While this model has worked in the past, there's no guarantee it will work in the future. The cryptocurrency market is changing, there are more participants, and institutional investor influence is growing. Use historical data for understanding, but not for precise predictions!
Halving's Impact on Miners
Halving isn't just a celebration for investors. For miners, this event brings serious challenges and can fundamentally change the industry landscape.
Mining Economics After Halving
Imagine: you're a miner who invested millions in equipment and pays huge electricity bills. And suddenly your income gets cut in half. Meanwhile, your expenses stay the same!
What happens after halving:
- Inefficient miners are forced to shut down equipment — it becomes unprofitable
- Network hashrate (total computing power) temporarily decreases
- Mining difficulty automatically adjusts to maintain ~10-minute block time
- Only the most efficient operations with cheap electricity and modern equipment survive
🔴 Losers
Miners with outdated equipment and expensive electricity. Their profit becomes negative, forcing them to exit the market.
🟢 Winners
Large industrial miners with access to cheap energy and the latest generation of ASIC miners. They capture the market share of departed competitors.
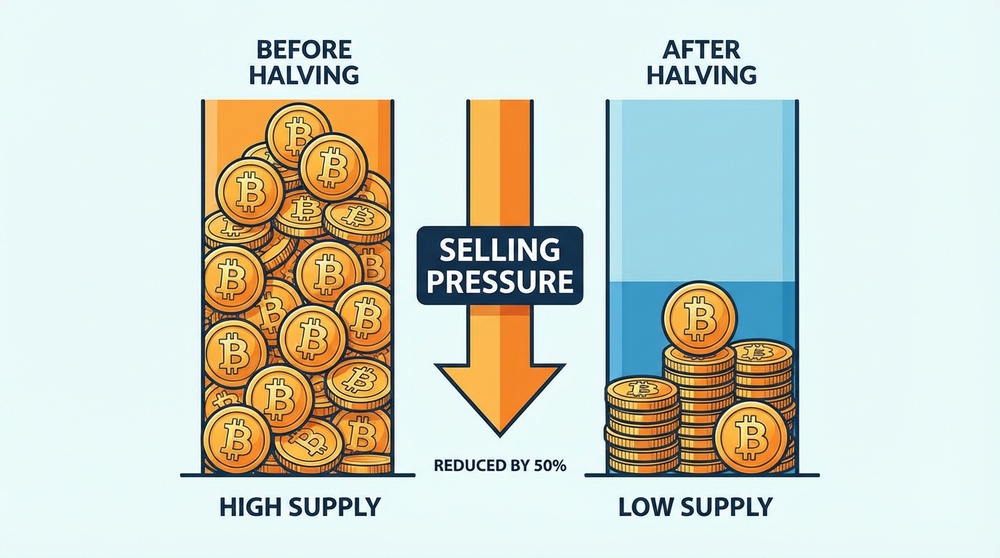
Sell Pressure
Miners are constant sellers in the Bitcoin market. They need to pay for electricity, salaries, rent, and other expenses. To do this, they regularly sell mined coins.
After halving, the number of new coins miners receive is cut in half. This means:
- Fewer bitcoins are put up for sale daily
- Seller pressure on the market decreases
- With sustained demand, this creates conditions for price growth
When Will All Halvings End?
One of the most intriguing questions: what happens when all bitcoins are mined?
Roadmap to 2140
Halvings will continue until the reward becomes so small that it reaches Bitcoin's minimum unit — 1 satoshi (0.00000001 BTC). After that, the emission of new coins will completely stop.
| Halving # | Approximate Year | Block Reward | % of BTC Mined |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2024 | 3.125 BTC | ~93.75% |
| 5 | 2028 | 1.5625 BTC | ~96.875% |
| 6 | 2032 | 0.78125 BTC | ~98.4375% |
| 10 | 2048 | ~0.05 BTC | ~99.9% |
| Last | ~2140 | 1 satoshi | 100% |
Amazing Fact
By the 2030s, over 99% of all bitcoins will already be mined. The remaining 1% will be "spread out" over the next 100+ years! This means the main emission is already practically complete, and we're living in an era when Bitcoin's scarcity is becoming maximum.
How Will the Network Work Without Block Rewards?
When block rewards end, miners will earn income only from transaction fees. This raises a legitimate question: will this be enough to maintain network security?
Several theories exist:
- Optimistic: By then, the value of one BTC will be so high that fees will be sufficient
- Technological: Development of Layer 2 solutions (Lightning Network) will change fee economics
- Pragmatic: The community has 100+ years to find a solution

Myths and Misconceptions About Halving
Many myths have formed around halving. Let's debunk the most common ones:
❌ Myth 1: "Price Always Rises Immediately After Halving"
Reality: History shows that significant growth usually occurs 6-18 months after the event, not immediately. At the moment of halving itself, the market may be neutral or even show a correction.
❌ Myth 2: "Halving Guarantees Growth"
Reality: Halving creates favorable conditions for growth (reduced supply), but doesn't guarantee it. Price is influenced by many factors: macroeconomics, regulation, competition, overall market sentiment.
❌ Myth 3: "Mining Will Die After Halving"
Reality: Mining adapts to new conditions. Less efficient players exit, but the industry continues to develop. Technology becomes more efficient, and price growth compensates for reduced rewards.
❌ Myth 4: "Halving Is Just a Marketing Event"
Reality: Halving is a real technical event programmed into Bitcoin's code. It cannot be canceled, postponed, or changed without the consent of the overwhelming majority of network participants.
💡 The Right Approach: View halving as one of the important factors affecting Bitcoin's fundamental value, but not as a magic "get rich" button. Invest based on deep understanding of the technology, not based on hype.
How to Prepare for Halving: Practical Tips
Now that you understand the mechanism and history of halvings, let's talk about practical actions:
For Investors
- Think long-term: Don't try to "catch" the exact moment. History shows that those who hold positions throughout the entire cycle benefit most
- Use DCA: Dollar-cost averaging strategy (regular purchases of a fixed amount) reduces timing risks
- Don't invest more than you can afford to lose: Even with a favorable halving, there can be significant corrections
- Diversify: Don't put all your eggs in one basket, even if that basket is Bitcoin
For Miners
- Optimize expenses: Look for cheaper electricity, upgrade equipment
- Build reserves: Accumulate BTC during high-profitability periods to survive difficult times
- Calculate your break-even point: Know at what BTC price your operation becomes unprofitable
For Everyone
- Education is your main tool: The better you understand the technology, the more rational your decisions
- Follow the news: But filter noise from signals
- Be patient: Cryptocurrency markets work on long time horizons
Halving in the Context of Global Economy
It's interesting to consider Bitcoin halving in the context of global economic trends:
Inflation vs Deflation
While central banks around the world print trillions of new money, Bitcoin moves in the opposite direction — its emission decreases. This creates a unique situation:
- Fiat currencies: Supply increases → purchasing power falls
- Bitcoin: Supply slows → potential for purchasing power growth
Institutional Recognition
With each halving, Bitcoin receives more attention from major institutional players: investment funds, banks, public companies. For them, halving is confirmation of the predictability and reliability of Bitcoin's monetary policy.
Institutional Interest
Unlike traditional assets, Bitcoin's monetary policy:
- Is completely transparent and predictable
- Doesn't depend on political decisions
- Cannot be changed to benefit specific interest groups
- Works 24/7/365 without weekends or holidays
For institutional investors, this reduces regulatory and political risks.
Technical Details for the Curious
For those who want to dive deeper, let's examine the technical side of halving:
How the Code Determines the Reward
In Bitcoin's source code, the reward is calculated using a simple formula:
Reward = 50 BTC / (2 ^ number_of_halvings)Where "number_of_halvings" = current block number / 210,000 (rounded down)
Examples:
- Block #100,000: 100,000 / 210,000 = 0 halvings → 50 / 2^0 = 50 BTC
- Block #300,000: 300,000 / 210,000 = 1 halving → 50 / 2^1 = 25 BTC
- Block #500,000: 500,000 / 210,000 = 2 halvings → 50 / 2^2 = 12.5 BTC
Why Exactly 21 Million?
The maximum number of bitcoins (21,000,000) is the result of halving mathematics:
If you add up all rewards for all blocks to infinity (accounting for halvings), you get a geometric progression:
210,000 × 50 × (1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + ...) = 210,000 × 50 × 2 = 21,000,000 BTC
This is an elegant mathematical solution that ensures predictable and limited emission.
Conclusion: Why Halving Matters to You
Let's summarize this comprehensive lesson:
Key Takeaways
- Halving is a programmed event where miner rewards are cut in half approximately every 4 years
- This creates controlled scarcity, making Bitcoin a rare asset with predictable monetary policy
- Historically, halvings have preceded significant price increases, though this doesn't guarantee future results
- Halving affects the entire ecosystem: miners, investors, developers, users
- By ~2140, all 21 million bitcoins will be mined, and emission will completely stop
Why This Matters Right Now
We're living in a unique time. Most bitcoins have already been mined, and with each halving, their emission becomes smaller. Understanding this mechanism gives you an advantage over most people who perceive cryptocurrencies as "incomprehensible magic."
🎓 Main Lesson: Halving isn't just an event to "survive" or "use for profit." It's a fundamental property of Bitcoin that distinguishes it from any other money in human history. Bitcoin is the first asset whose monetary policy is known in advance and unchangeable. And halving is the key element of this uniqueness.
In the next lesson, we'll dive into the "Crypto Slang Dictionary" and break down popular crypto community jargon: what HODL, FOMO, FUD mean, and who "whales" and "paper hands" are. See you there! 🚀